Let's scrap Internet with Scrapy
20200501Internet contains the most universal data resource so far in the history, so many of them are free for any users.
However, due to the variety of different webpages, these are hard to be collected and reused by group.
To fetch the data from pages, we may need to analyse the webpages’ structure and evaluate the data to fetch.
The process of this is called “web scraping”, it is the most important task of the any web search engines.
Also, the users can be benefited by making their scrapers to fetch the required data collections from the sea.
Scrapy introduction:
Scrapy is a popular web crawler framework by Python, it contains many modules with solid mechanism
to provide a simplified and completed web scraping solutions. To start using Scrapy, we can install by pip.
pip install scrapy
After installed and open the help page, we can see that,
$ scrapy -h
Scrapy 2.0.1 - no active project
Usage:
scrapy <command> [options] [args]
Available commands:
bench Run quick benchmark test
fetch Fetch a URL using the Scrapy downloader
genspider Generate new spider using pre-defined templates
runspider Run a self-contained spider (without creating a project)
settings Get settings values
shell Interactive scraping console
startproject Create new project
version Print Scrapy version
view Open URL in browser, as seen by Scrapy
[ more ] More commands available when run from project directory
Use "scrapy <command> -h" to see more info about a command
Normally to develop a web scraper to use, the following commands will be used,
-
startproject <project_name> [project_dir]: a Python project structured folder will be generated to kick off -
genspider [options] <name> <domain>: generate a templated spider, supported HTML, XML and CSV as well -
shell [url|file]: boot the interactive console(IPython) with the given url or file scraped, very useful for develop -
runspider [options] <spider_file>: run a spider, resulted with scraped data and JSON, CSV records
For more details, refering from the official documents would never be a bad choice.
Scrapy workflow:
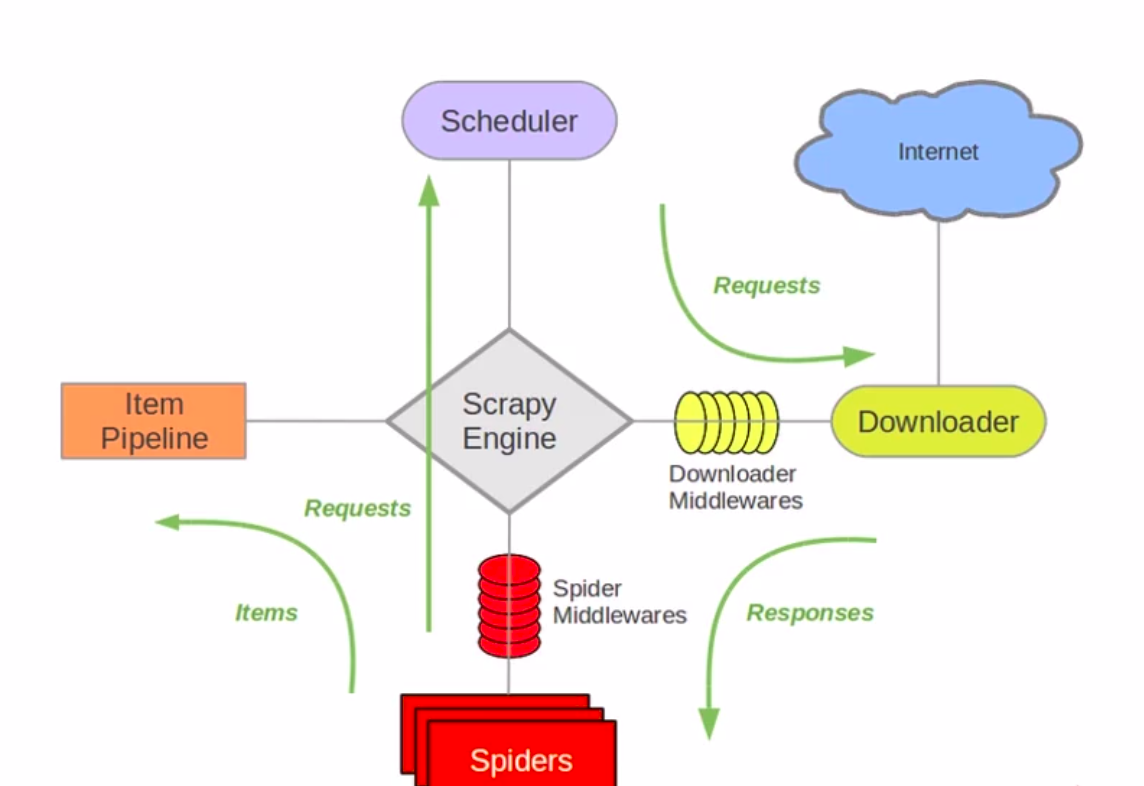
Generally, when a spider started to crawl webpages using Scrapy, the engine will be operated on as follow,
-
The spider sends the URL requests to crawl and queued in the scheduler
-
The scheduler passes the next request to downloader and response through the downloader middlewares
-
The spider receives the downloader’s response objects and returns scraped items through the spider middlewares
-
The item pipeline set will handle the processed items from spider then output to the external
P.S: The process repeats until there are no more requests from the scheduler’s queue list
